Consider me your AI tool-testing guinea pig.
Every week, I test hundreds of AI tools and report the best ones- so you don't have to.
Here are the top 10 most useful AI tools of the week (all new):
Rowan Cheung
@rowancheung
1. Inflection Pi
Pi, or 'personal intelligence' is a ChatGPT competitor designed to offer concise information, friendly advice, and conversations.

 heypi.com
heypi.com
·
4h
2. Nyric
A new text-to-3D world generation platform in Unreal Engine.
Soon, we'll be able to create entire games in seconds from text prompts using AI.
4h
3. Dream3D
A new YC-backed 3D design tool making it easy for anyone to create beautiful computer graphics.
·
4h
4. Portfolio Pilot
The first verified ChatGPT plugin for investing.
Supported by hedge fund models, the plugin is already accessible to those with plugin access.
·
4h
5. AudioPen
The easiest way to convert messy thoughts into clear text.
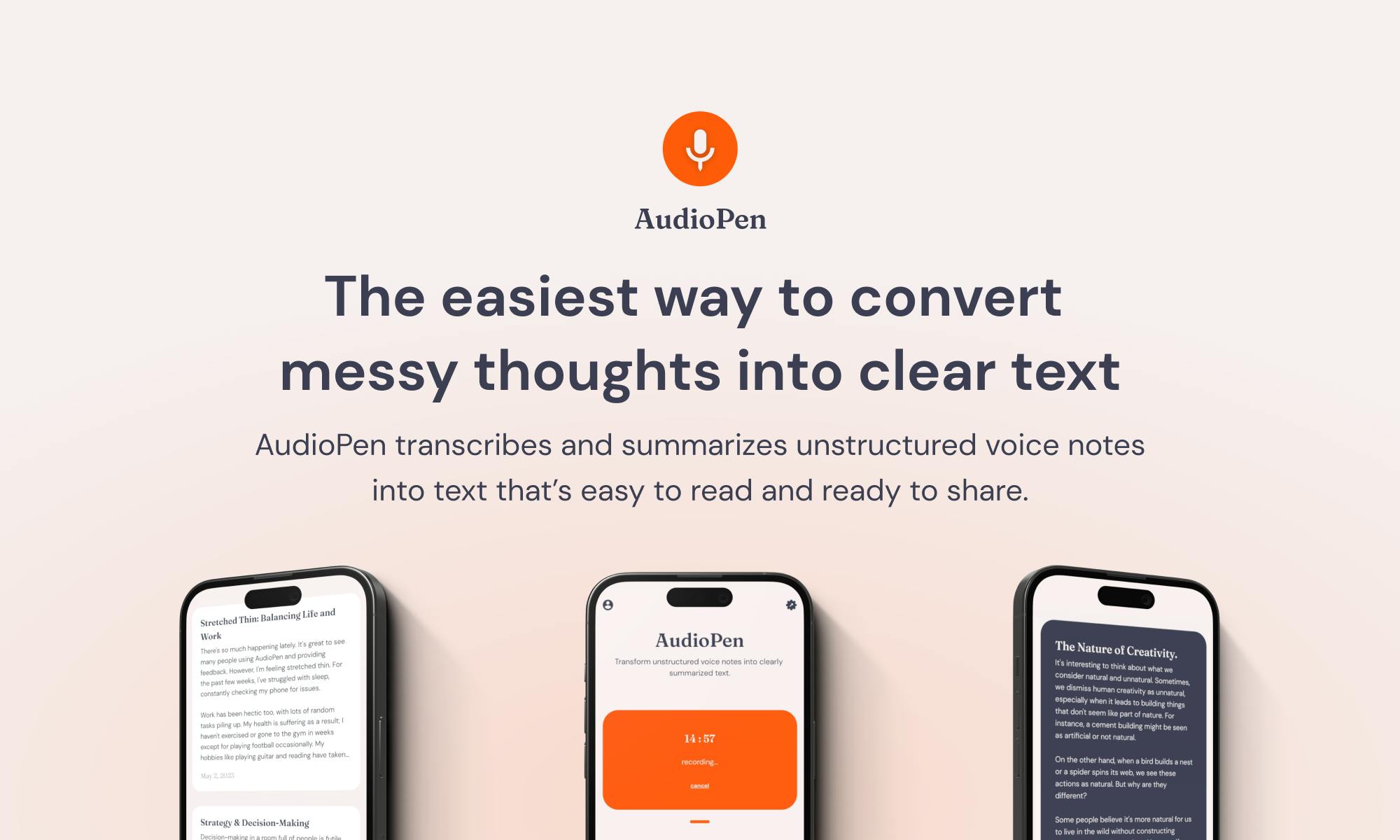
 audiopen.ai
audiopen.ai
Every week, I test hundreds of AI tools and report the best ones- so you don't have to.
Here are the top 10 most useful AI tools of the week (all new):
Rowan Cheung
@rowancheung
1. Inflection Pi
Pi, or 'personal intelligence' is a ChatGPT competitor designed to offer concise information, friendly advice, and conversations.

Pi, your personal AI
Hi, I'm Pi. I'm your personal AI, designed to be supportive, smart, and there for you anytime. Ask me for advice, for answers, or let's talk about whatever's on your mind.
 heypi.com
heypi.com
·
4h
2. Nyric
A new text-to-3D world generation platform in Unreal Engine.
Soon, we'll be able to create entire games in seconds from text prompts using AI.
4h
3. Dream3D
A new YC-backed 3D design tool making it easy for anyone to create beautiful computer graphics.
·
4h
4. Portfolio Pilot
The first verified ChatGPT plugin for investing.
Supported by hedge fund models, the plugin is already accessible to those with plugin access.
·
4h
5. AudioPen
The easiest way to convert messy thoughts into clear text.

AudioPen | The easiest way to convert messy thoughts into clear text
AudioPen transcribes and summarizes unstructured voice notes into text that’s easy to read and ready to share. If you like thinking out loud, you'll love Audio Pen. It's like having a personal assistant who records and summarizes your thoughts.
 audiopen.ai
audiopen.ai