As crime dries up, Japan’s police hunt for things to do
As crime dries up, Japan’s police hunt for things to do
There was just one fatal shooting in the whole of 2015
As crime dries up, Japan’s police hunt for things to do
As crime dries up, Japan’s police hunt for things to do
There was just one fatal shooting in the whole of 2015
7 minutes ago
There was just one fatal shooting in the whole of 2015
THE stake-out lasted a week, but it paid off in the end. The tireless police of Kagoshima, a sleepy city in the far south of the country, watched the unlocked car day and night. It was parked outside a supermarket, and contained a case of malt beer. Finally, a passing middle-aged man decided to help himself. Five policemen instantly pounced, nabbing one of the city’s few remaining law-breakers.
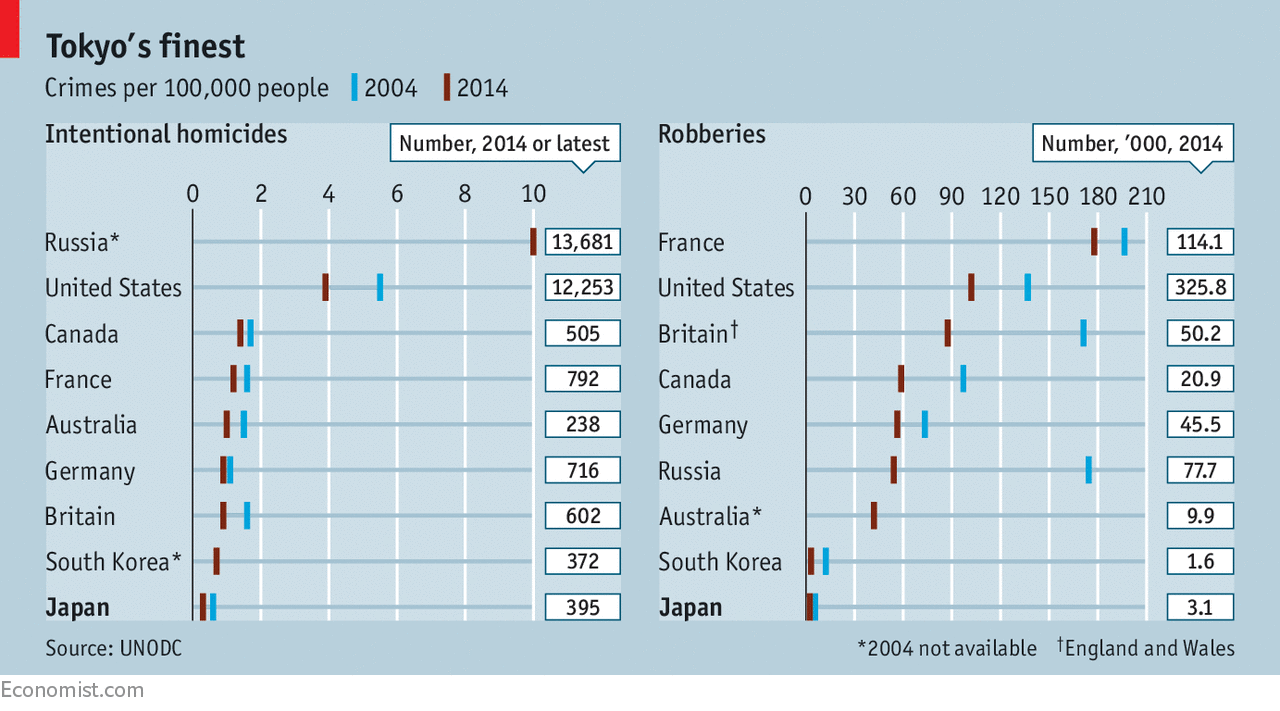
Japan’s cluttered streets are not always pretty but they are remarkably safe. Crime rates have been falling for 13 years. The murder rate of 0.3 per 100,000 people is among the lowest in the world; in America it is almost 4 (see chart). A single gun slaying was recorded for the whole of 2015. Even
yakuza gangsters, once a potent criminal force, have been weakened by tougher laws and old age.
Yet, far from being pensioned off, the police are growing in numbers: beat cops, known colloquially as
omawari-san (Mr Walk-around), are a fixture in most neighbourhoods. Japan has over 259,000 uniformed officers—15,000 more than a decade ago, when crime rates were far higher. The ratio of officers to population is very high, especially in Tokyo, home to the world’s biggest metropolitan police force—a quarter bigger than the one protecting New York.
This means plenty of attention for crimes that would be considered too petty to investigate elsewhere, such as the theft of a bicycle or the possession of a tiny amount of drugs. One woman describes how five officers crowded into her cramped apartment after she reported her knickers being swiped from a clothesline. A small army of detectives was assigned last year to apprehend a group of 22 people who had been growing marijuana for their personal use only and smoking it in deserted rural spots.
In fact, as the police run out of things to do, they are becoming more inventive about what constitutes a crime, says Kanako Takayama of Kyoto University. In one recent case, she says, they arrested a group of people who had shared the cost of renting a car, deeming the arrangement an illegal taxi. Some prefectures have begun prosecuting people who ride their bicycles through red lights.
In 2015 a man was arrested for scribbling Adolf Hitler moustaches onto posters of Shinzo Abe, the prime minister. Ms Takayama says detectives have started appearing without permission on university campuses, to monitor “troublesome” students. One reason why police are going after cyclists may be to make up for the steady fall in driving offences. (Both drivers and cyclists can avoid fines by signing up for remedial training at certified driving schools, which are often staffed by retired officers, notes Colin Jones of Doshisha University.) Fifteen years ago police in Hokkaido, in Japan’s sparsely populated north, conspired with
yakuza gangsters to smuggle guns into the country so they could meet quotas for finding them.
The hunt for things to do may sometimes be beneficial. The number of reported cases of children being abused at home has almost doubled since 2010, despite the declining birth rate. That suggests the police are increasingly intervening in the domestic sphere, which they used to avoid.
Even critics of Japan’s justice system accept that it gets a lot right. Rates of recidivism are low and a great deal of effort is made to keep young offenders out of the prison system; police work with parents to keep young people on the straight and narrow. Adults are incarcerated at a far lower rate than in most rich countries: 45 per 100,000, compared with 146 in Britain and 666 in the United States.
Yet the police are oddly inefficient. Even though there are so many officers and so few crimes, they solve less than 30% of them. Confessions, often made under duress, form the basis of most criminal prosecutions. The courts dismissed the case of the beer thief in Kagoshima, despite all the work that went into it. Japan is almost crime-free not thanks to the police, says Yoshihiro Yasuda, a campaigning lawyer, but because people police themselves.
This article appeared in the Asia section of the print edition under the headline "Petty officers"


 Thread full of Lou Pickles "we used to walk 15 miles" babble.
Thread full of Lou Pickles "we used to walk 15 miles" babble.