Stability AI releases DeepFloyd IF, a powerful text-to-image model that can smartly integrate text into images — Stability AI
DeepFloyd IF is a state-of-the-art text-to-image model released on a non-commercial, research-permissible license that allows research labs to examine and experiment with advanced text-to-image generation approaches. In line with other Stability AI models, Stability AI intends to release a DeepFloyd
Stability AI releases DeepFloyd IF, a powerful text-to-image model that can smartly integrate text into images
28 AprToday Stability AI, together with its multimodal AI research lab DeepFloyd, announced the research release of DeepFloyd IF, a powerful text-to-image cascaded pixel diffusion model.
DeepFloyd IF is a state-of-the-art text-to-image model released on a non-commercial, research-permissible license that provides an opportunity for research labs to examine and experiment with advanced text-to-image generation approaches. In line with other Stability AI models, Stability AI intends to release a DeepFloyd IF model fully open source at a future date.
Description and Features
- Deep text prompt understanding:
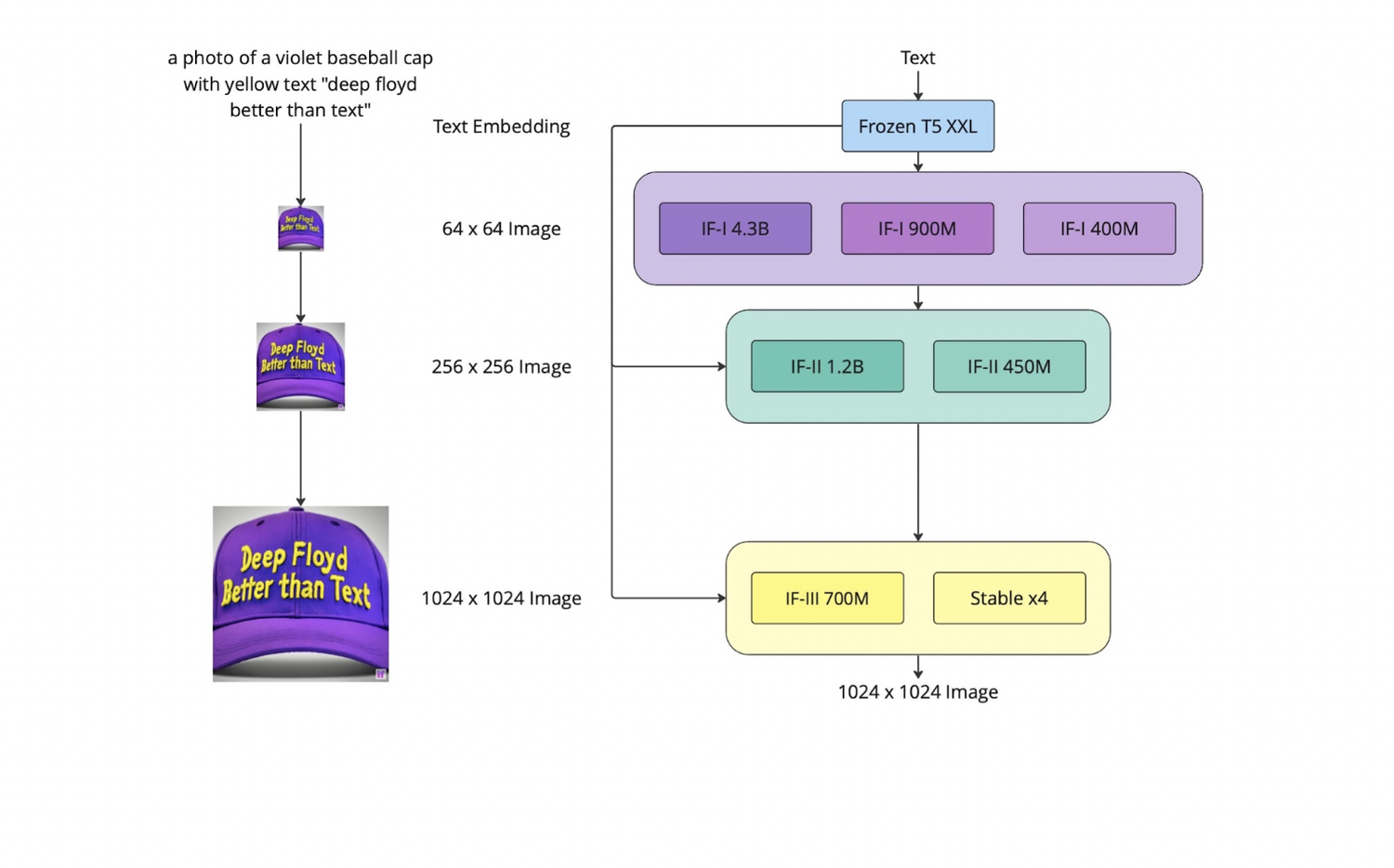
The generation pipeline utilizes the large language model T5-XXL-1.1 as a text encoder. A significant amount of text-image cross-attention layers also provides better prompt and image alliance. - Application of text description into images:
Incorporating the intelligence of the T5 model, DeepFloyd IF generates coherent and clear text alongside objects of different properties appearing in various spatial relations. Until now, these use cases have been challenging for most text-to-image models. - A high degree of photorealism:
This property is reflected by the impressive zero-shot FID score of 6.66 on the COCO dataset (FID is a main metric used to evaluate the performance of text-to-image models; the lower the score, the better). - Aspect ratio shift:
The ability to generate images with a non-standard aspect ratio, vertical or horizontal, as well as the standard square aspect. - Zero-shot image-to-image translations:
Image modification is conducted by (1) resizing the original image to 64 pixels, (2) adding noise through forward diffusion, and (3) using backward diffusion with a new prompt to denoise the image (in inpainting mode, the process happens in the local zone of the image). The style can be changed further through super-resolution modules via a prompt text description. This approach gives the opportunity to modify style, patterns and details in output while maintaining the basic form of the source image – all without the need for fine-tuning.

View fullsize

View fullsize

View fullsize

View fullsize

View fullsize

Definitions and processes
DeepFloyd IF is a modular, cascaded, pixel diffusion model. We break down the definitions of each of these descriptors here:
- Modular:
DeepFloyd IF consists of several neural modules (neural networks that can solve independent tasks, like generating images from text prompts and upscaling) whose interactions in one architecture create synergy.
- Cascaded:
DeepFloyd IF models high-resolution data in a cascading manner, using a series of individually trained models at different resolutions. The process starts with a base model that generates unique low-resolution samples (a ‘player’), then upsampled by successive super-resolution models (‘amplifiers’) to produce high-resolution images.
- Diffusion:
DeepFloyd IF’s base and super-resolution models are diffusion models, where a Markov chain of steps is used to inject random noise into data before the process is reversed to generate new data samples from the noise.
- Pixel:
DeepFloyd IF works in pixel space. The diffusion is implemented on a pixel level, unlike latent diffusion models (like Stable Diffusion), where latent representations are used.