Lumiere generates five-second videos that "portray realistic, diverse and coherent motion."

arstechnica.com
Google’s latest AI video generator can render cute animals in implausible situations
Lumiere generates five-second videos that "portray realistic, diverse and coherent motion."
BENJ EDWARDS - 1/24/2024, 5:45 PM
Enlarge / Still images of AI-generated video examples provided by Google for its Lumiere video synthesis model.
Google
On Tuesday, Google announced
Lumiere, an AI video generator that it calls "a space-time diffusion model for realistic video generation" in the
accompanying preprint paper. But let's not kid ourselves: It does a great job of creating videos of cute animals in ridiculous scenarios, such as using roller skates, driving a car, or playing a piano. Sure, it can do more, but it is perhaps the most advanced text-to-animal AI video generator yet demonstrated.
FURTHER READING
Google’s newest AI generator creates HD video from text prompts
According to Google, Lumiere utilizes unique architecture to generate a video's entire temporal duration in one go. Or, as the company put it, "We introduce a Space-Time U-Net architecture that generates the entire temporal duration of the video at once, through a single pass in the model. This is in contrast to existing video models which synthesize distant keyframes followed by temporal super-resolution—an approach that inherently makes global temporal consistency difficult to achieve."
In layperson terms, Google's tech is designed to handle both the space (where things are in the video) and time (how things move and change throughout the video) aspects simultaneously. So, instead of making a video by putting together many small parts or frames, it can create the entire video, from start to finish, in one smooth process.
The official promotional video accompanying the paper "Lumiere: A Space-Time Diffusion Model for Video Generation," released by Google.
Lumiere can also do plenty of party tricks, which are laid out quite well with examples on
Google's demo page. For example, it can perform text-to-video generation (turning a written prompt into a video), convert still images into videos, generate videos in specific styles using a reference image, apply consistent video editing using text-based prompts, create
cinemagraphs by animating specific regions of an image, and offer video
inpainting capabilities (for example, it can change the type of dress a person is wearing).
In the Lumiere research paper, the Google researchers state that the AI model outputs five-second-long 1024×1024 pixel videos, which they describe as "low-resolution." Despite those limitations, the researchers performed a user study and claim that Lumiere's outputs were preferred over existing AI video synthesis models.
As for training data, Google doesn't say where it got the videos it fed into Lumiere, writing, "We train our T2V [text to video] model on a dataset containing 30M videos along with their text caption. [sic] The videos are 80 frames long at 16 fps (5 seconds). The base model is trained at 128×128."
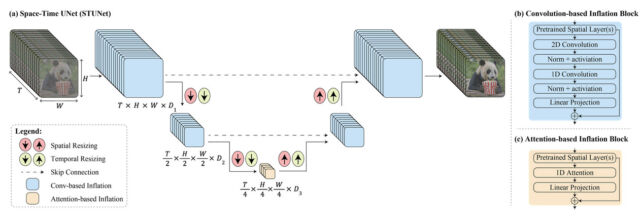 Enlarge / A block diagram showing components of the Lumiere AI model, provided by Google.
Google
Enlarge / A block diagram showing components of the Lumiere AI model, provided by Google.
Google
AI-generated video is still in a primitive state, but it has been progressing in quality over the past two years. In October 2022, we covered Google's first publicly unveiled image synthesis model,
Imagen Video. It could generate short 1280×768 video clips from a written prompt at 24 frames per second, but the results weren't always coherent. Before that, Meta debuted its AI video generator,
Make-A-Video. In June of last year, Runway's Gen2 video synthesis model enabled the creation of two-second video clips from text prompts, fueling the creation of
surrealistic parody commercials. And in November, we covered
Stable Video Diffusion, which can generate short clips from still images.
AI companies often demonstrate video generators with cute animals because generating coherent, non-deformed humans is currently difficult—especially since we, as humans (you are human, right?), are adept at noticing any flaws in human bodies or how they move. Just look at AI-generated
Will Smith eating spaghetti.
FURTHER READING
AI-generated video of Will Smith eating spaghetti astounds with terrible beauty
Judging by Google's examples (and not having used it ourselves), Lumiere appears to surpass these other AI video generation models. But since Google tends to keep its AI research models close to its chest, we're not sure when, if ever, the public may have a chance to try it for themselves.
As always, whenever we see text-to-video synthesis models getting more capable, we can't help but think of the
future implications for our Internet-connected society, which is centered around sharing media artifacts—and the general presumption that "realistic" video typically represents real objects in real situations captured by a camera. Future video synthesis tools more capable than Lumiere will make deceptive deepfakes trivially easy to create.
To that end, in the "Societal Impact" section of the Lumiere paper, the researchers write, "Our primary goal in this work is to enable novice users to generate visual content in an creative and flexible way. [sic] However, there is a risk of misuse for creating fake or harmful content with our technology, and we believe that it is crucial to develop and apply tools for detecting biases and malicious use cases in order to ensure a safe and fair use."