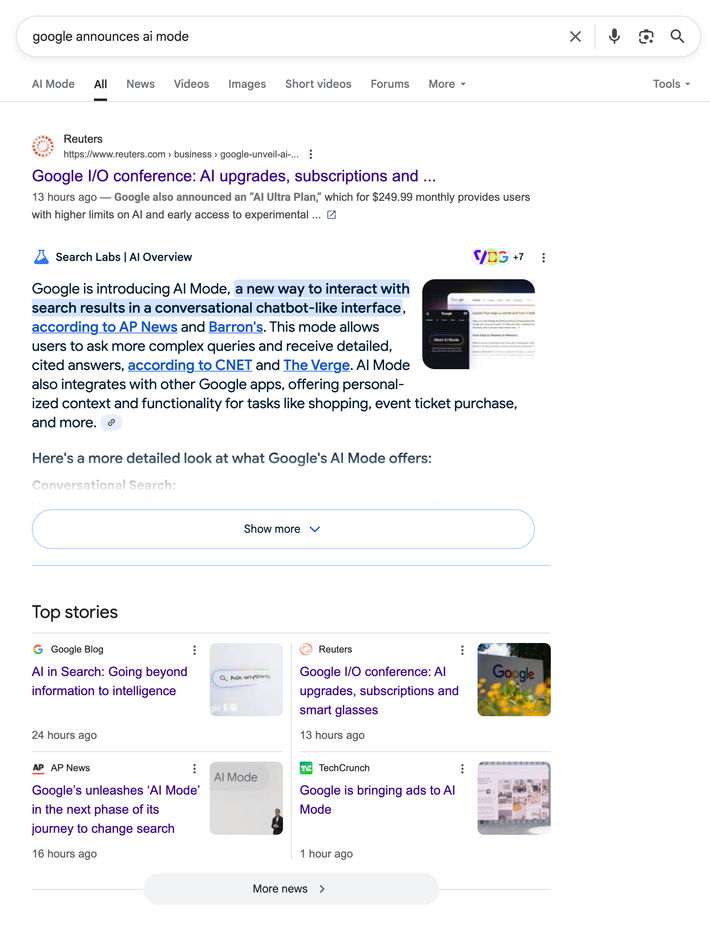
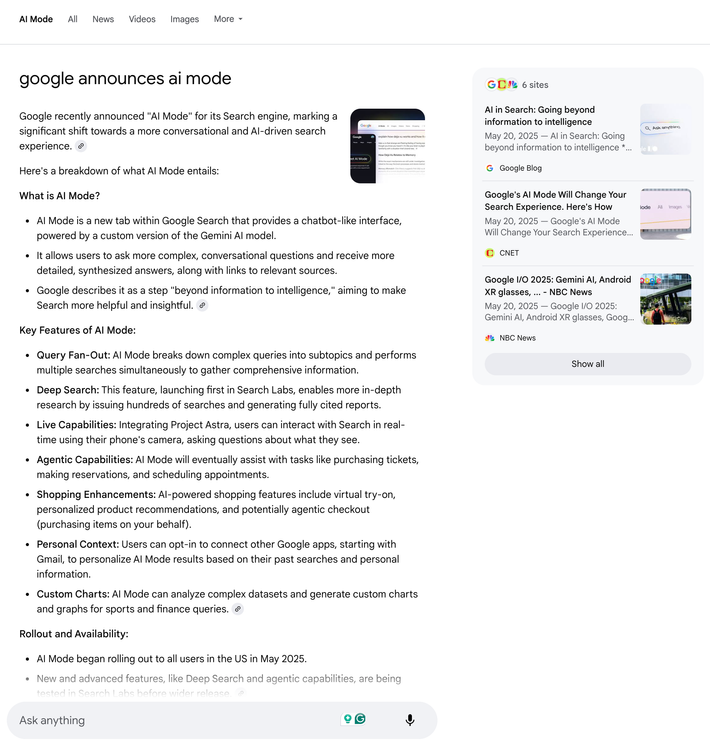
An analysis done by
Copyleaks, an AI and plagiarism detection software company, at the request of CNET, found that only 12 pages on Mother Earth Travel used AI-generated content. Copyleaks' president of marketing, Eric Bogard, says it's possible that Mother Earth Travel is running its content through another software to bypass AI detection software, but wouldn't go so far as to say the site is engaging in AI-assisted plagiarism. Despite the site's strong placement in Google Search and its entire suite of articles being authored by one person, the site denies using AI. It said it has a team of writers but uses only one byline to protect their privacy.
"We, by principle and deed, are 100% 'white-hat' and don't take any short-cuts or do anything nefarious (including slinging mud at competitors)," said Shawn Shafai of Mother Earth Travel to CNET in a lengthy statement.
Hake's situation shows how difficult it is for online creators to make content when they're being squeezed by Google's search algorithm, Google's own AI summary tools and new sites that produce similar content bylined by a single person.
Spam is something Google's been fighting since its very inception, according to Thompson, and the company issued an update in
March to address the latest wave of manmade and automated content abuse.
Review sites can't escape Google's algorithm
Gisele Navarro, managing editor at
HouseFresh, experienced the
repercussions of Google's Product Reviews Update in late 2023. This update was meant to elevate actual human reviews of products and push down junk content. What this ended up doing was hoisting larger, more established brands and demoting sites like HouseFresh, which work hard to buy and review air quality products.
"We were 15, including full-time and contractors, and we had to immediately just reduce the number of articles that we were publishing and the number of products that we could buy because we just couldn't afford it," said Navarro.
According to Navarro's post, some sites are using their position on the internet to pump out "best lists" -- for instance, best air purifiers and best headphones of 2024 -- with little actual product testing. BuzzFeed, for example, doesn't test all products but looks at
what people have said in their Amazon reviews and compiles a list. Rolling Stone
follows a similar practice for some pieces.
"Because these are very big, authoritative sites in the SEO space, they get to rank really well," said Lily Ray, vice president of SEO strategy and research at Amsive, a marketing agency. Ray's been vocal about SEO abuses on X, the social media platform formerly known as Twitter, and has highlighted sites that have abused their position. "Forbes's 'the best CBD gummies of 2024' -- they're literally going to be ranked number one above a dispensary website, right? That's what people have a lot of issue with."
Forbes has been the target of site owners and SEO experts as a publication benefiting from its ranking within Google on a wide range of topics, from CBD gummies, to air purifiers and even best pet insurance. Forbes disagrees with critics, arguing it's simply doing its journalistic duty in giving its readers content they desire.
"Forbes adheres to Google's policies, and we have not been penalized for site reputation abuse," said Laura Brusca, Forbes' chief communications officer, in a statement to CNET. "Our success and visibility reflect the substantial investment we make each year in producing high-quality, expert-written content that aligns with the topics we're covering and what our audience wants."
In all fairness, CNET too publishes a wide range of recommendation articles seemingly outside its core tech-focused brand, such as a list of the
best solar panel installation companies in Houston (as well as a variety of other cities) and the
best meal delivery services. CNET's product reviews and best lists generate money for the site via affiliate links, which funds our journalism. CNET employs reviewers who adhere to
standards of credibility, fairness and editorial independence and follows
testing procedures, often in dedicated labs, before making recommendations. Companies have no editorial control over what's published.
To battle site reputation abuse, Google pushed out a policy
earlier this May and
one last month. These are manual actions taken by Google in which employees will penalize sites that are abusing their position on the internet to push out low-quality content.
Although HouseFresh's traffic has gotten better, pleas from Navarro to Google haven't prompted the turnaround in traffic she was hoping for.
Google invites site owners to break bread but leaves them feeling hungry
After more than a year of outcry from site owners and SEO experts, Google decided it needed to talk to people in person. The company organized a meeting at its offices in Mountain View, California, in late October. It invited sites like HouseFresh, Giant Freakin' Robot, Travel Lemming and others to discuss, and possibly fix, Search.
The meeting with Navarro and other creators at Google's California headquarters was confrontational. While Google was apologetic about the affects algorithmic changes had on sites, there was a level of denialism coming from its engineers, according to Navarro.
"Whatever is happening to sites like ours seems like a mystery to them," said Navarro. "They denied there was some sort of site wide classifier drowning our domains and doubled down on the fact that the algorithm works on pages and not entire domains. However, many of the creators in the room had multiple examples of their sites being clearly shadowbanned."
Shadowbanning is a term in the social media space meaning to be made invisible to other users. A shadowbanned account still exists on the platform but isn't readily visible or is pushed down by the algorithm. It's a more subtle form of banishment that doesn't outright delete an account but greatly diminishes their influence or reach. It's often used against bad actors posting negative content or engaging in abusive behavior.
Google had a more positive outlook following the meeting with creators, saying it was an opportunity for open dialogue with creators and finding ways to improve, according to Thompson.
While Navarro found the meeting in Mountain View to be a mixed bag, Joshua Tyler, founder of Cinemablend and Giant Freakin Robot,
equated it to a funeral in a blog post about the event. Tyler had a more combative back-and-forth with Pandu Nayak, Google's vice president of Search, with Nayak denying that Tyler's site, or any sites in attendance, had been shadowbanned because Google's ranking comes down to the individual page level.
When site owners pushed back saying their sites were deranked simultaneously over a single night, Nayak was nonplussed, giving confused looks to anyone who disagreed.
"[Google said] without an ounce of pity or concern that there would be updates but he didn't know when they'd happen or what they'd do," according to Tyler's blog post. "Further questions on the subject were met with indifference as if he didn't understand why we cared."
Not everyone was as dejected as Tyler and Navarro. Hake from Travel Lemming was also at Google's creator summit and found the
hours of conversations with Google's Search engineers as helpful. He was less enthused with Nayak's responses around AI and ultimately believes, like other creators, that it's best not to assume Google will fix things for creators.
"The Google speakers at the event reinforced that they were there to listen and hear feedback, and that they were very grateful for the ongoing dialogue with creators," Davis said in a statement when asked if Nayak would like to give a response. "The speakers made it clear that while Google can't make any guarantees to specific sites, we absolutely look to understand if and how we can do better in surfacing high quality, helpful content for people."
Tyler announced earlier this month that he'd be
shutting down Giant Freakin Robot and would instead focus on the site's
YouTube channel. Saltalamacchia will continue working on RetroDodo but has a new part-time gig with
Kagi, a paid search engine billing itself as a private alternative to Google.
"First, they'd have had to acknowledge there was a problem, which they did not," said Tyler in an email with CNET. He went on to say that the teams within Google, like search and ads, seem siloed and are unaware about how things work in different parts of the company and had to spend time explaining YouTube analytics to some of Google's engineers. "Further, I also got a clear indication from Google that things aren't going to get any better, which was in its own way helpful."
Tyler's laid off his entire staff and is saddened by the idea that after 24 years of digital journalism, it'd be coming to an end because of Google's alleged shadowban. At the very least, Google told Tyler that there wasn't anything wrong with Giant Freakin Robot, which allowed him to stop agonizing over his own actions.
"My hope is that, despite Google telling us nothing will change, all the light shined on the situation by the attendees who were with me at the Google Creator Event may have changed their mind," said Tyler. "This core update is their chance, perhaps their last chance, to reverse course."