
‘So Much Death’: Lawmakers Weigh Stricter Speed Limits, Safer Roads for Pedestrians - KFF Health News
New York and Michigan recently passed laws allowing local jurisdictions to lower speed limits, and Los Angeles voters backed safer road designs, but enforcement often meets political resistance. The number of pedestrians killed or injured on the road remains high.

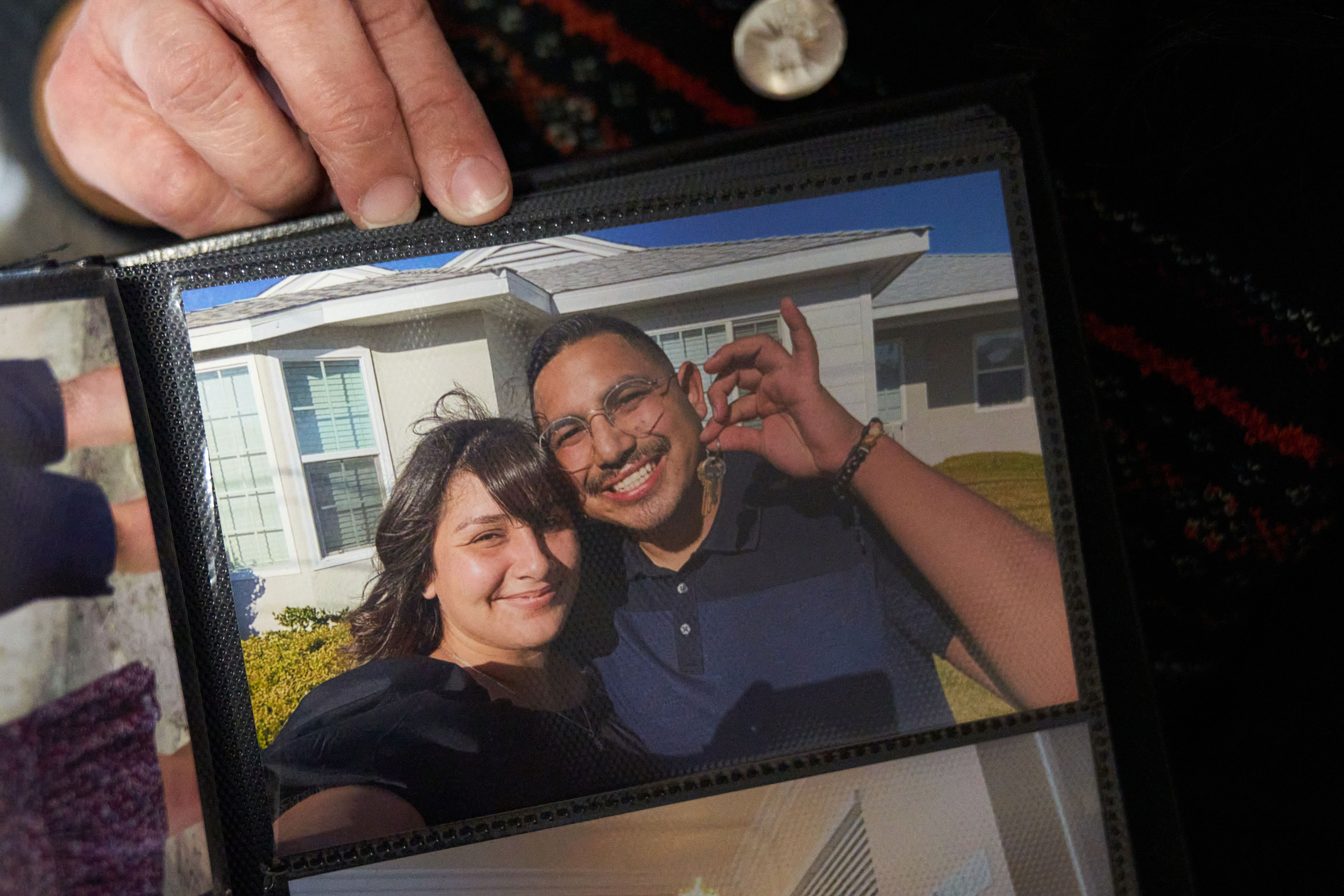
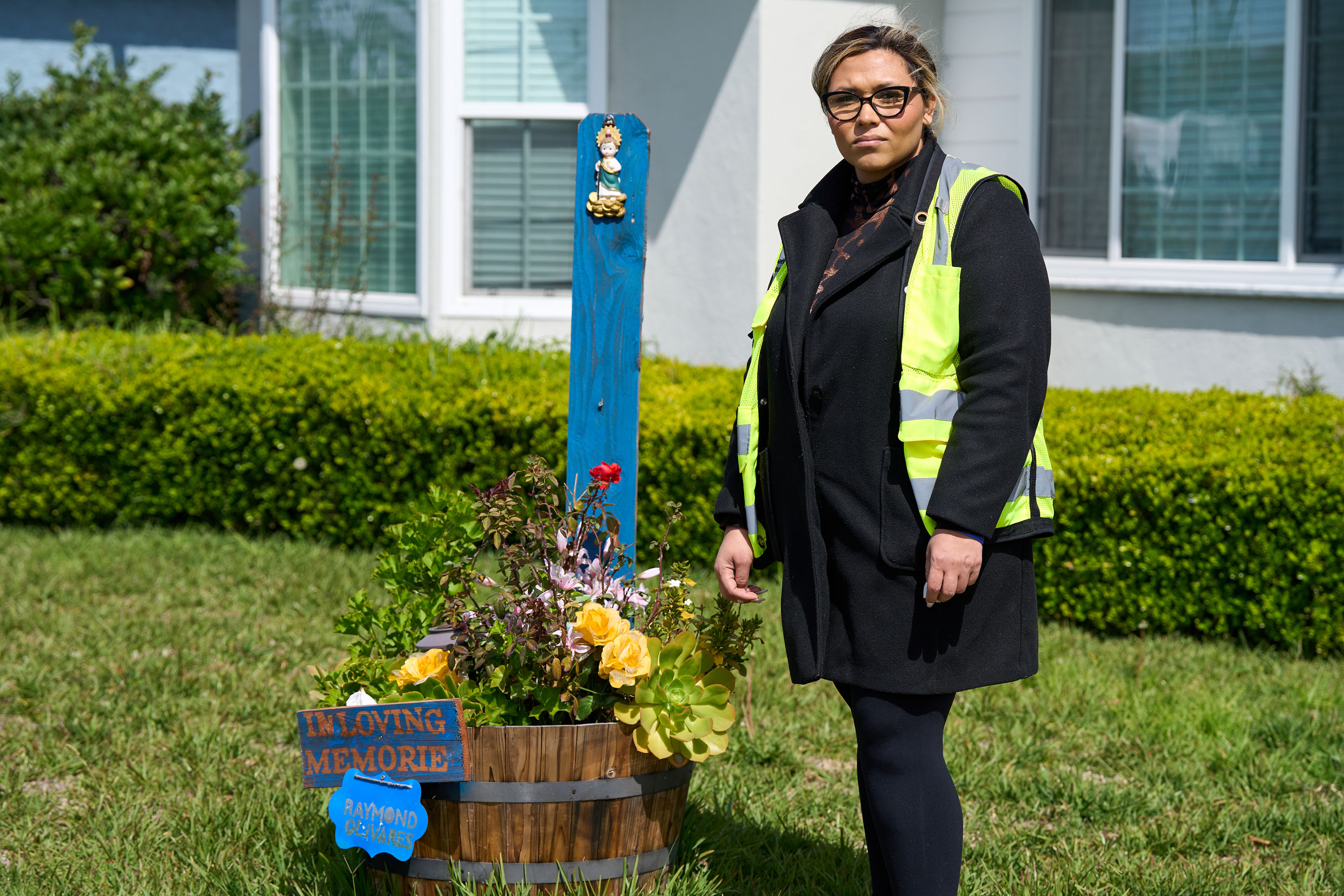
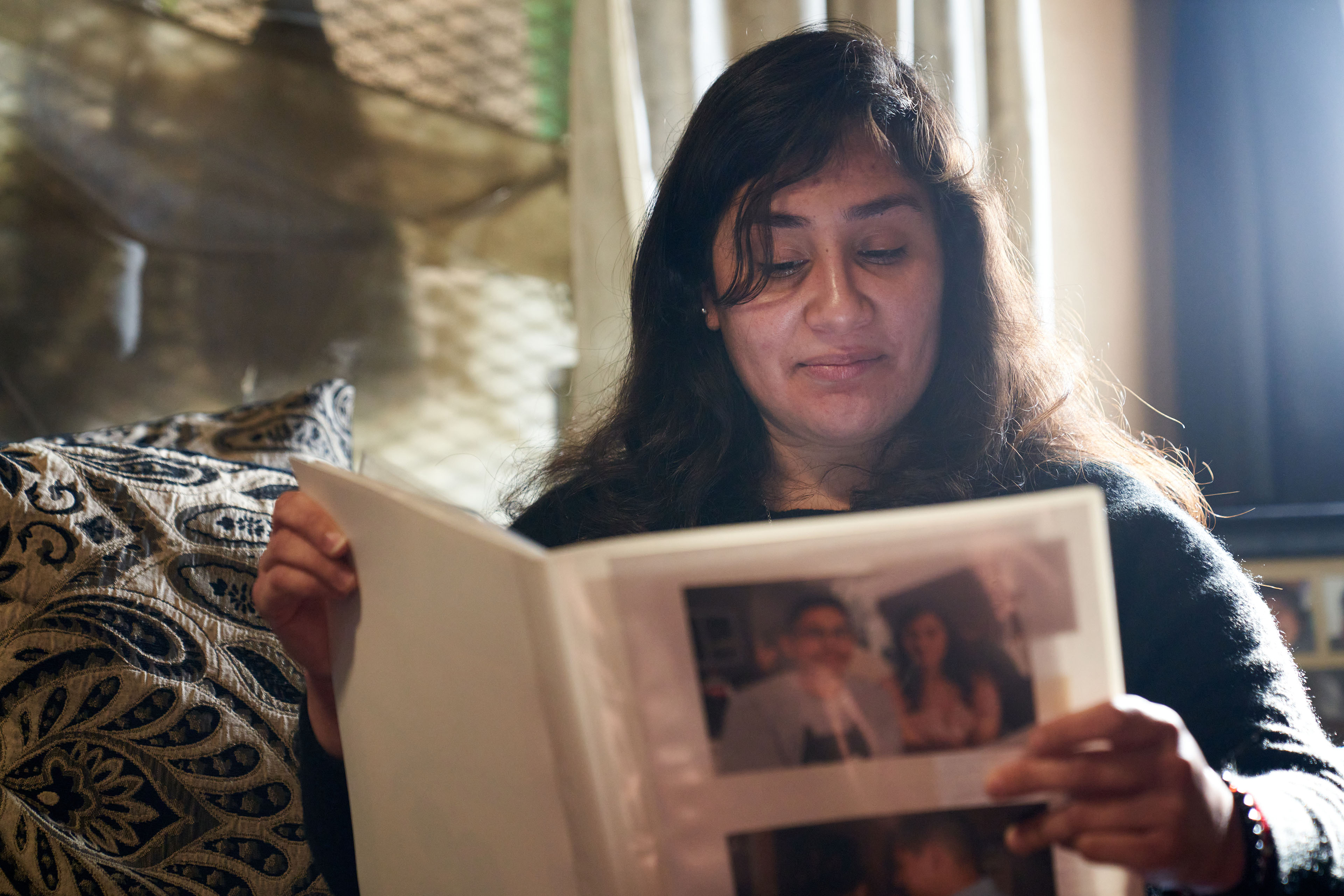
María Rivas Cruz looks through a scrapbook of memories from her more than a decade-long relationship with Raymond Olivares, who died last year after being struck by a speeding car. The photo she holds shows them celebrating buying a house together. (Lauren Justice for KFF Health News)
‘So Much Death’: Lawmakers Weigh Stricter Speed Limits, Safer Roads for Pedestrians
By Vanessa G. Sánchez June 3, 2024
LOS ANGELES — The party was winding down. Its young hosts, María Rivas Cruz and her fiancé, Raymond Olivares, had accompanied friends to their car to bid them farewell. As the couple crossed a four-lane main road back to the home they had just bought, Rivas Cruz and Olivares were struck by a car fleeing an illegal street race. The driver was going 70 in a 40-mph zone.
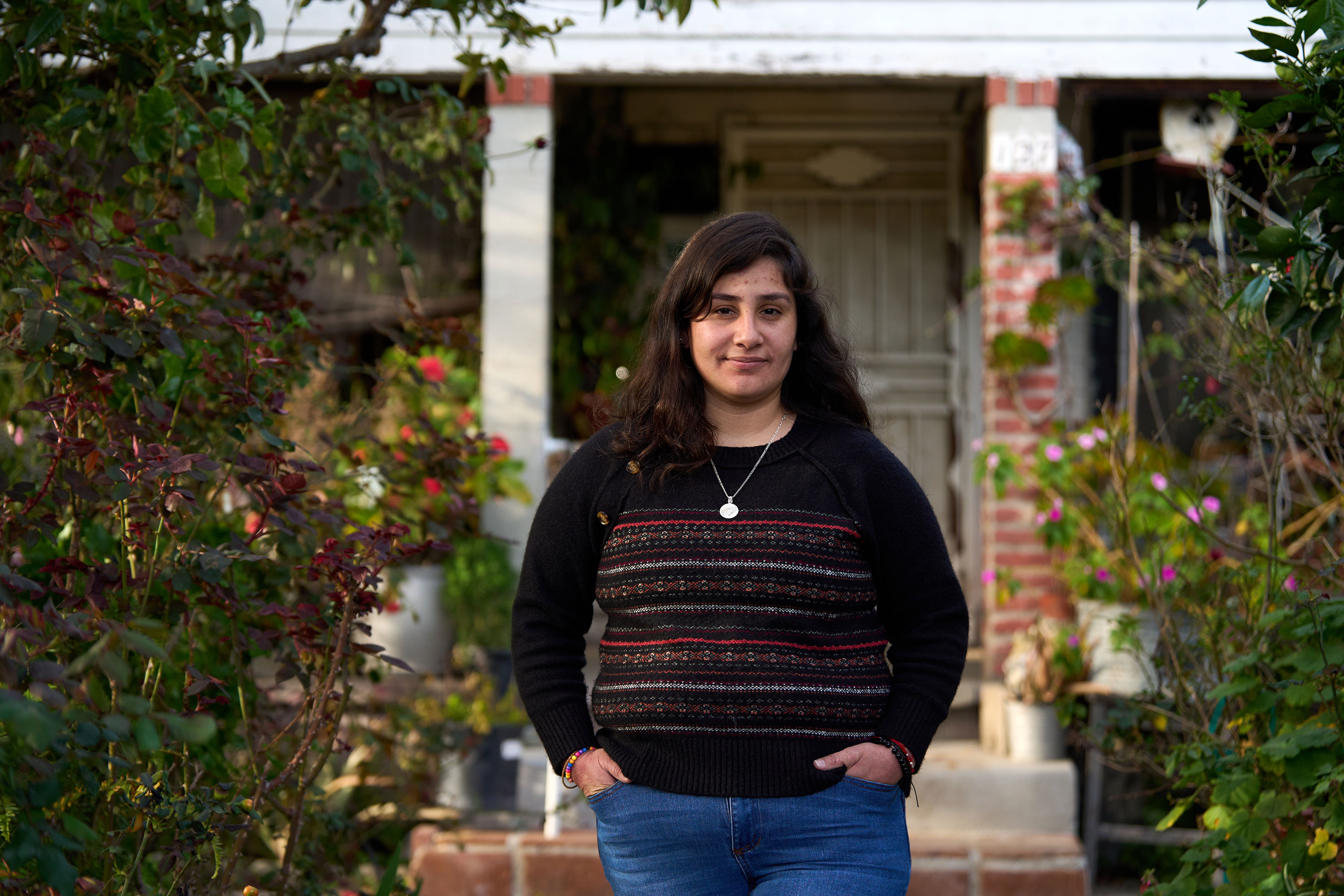
Despite years of pleading for a two-lane road, lower speed limits, safety islands, and more marked crosswalks, residents say the county had done little to address speeding in this unincorporated pocket of southeastern Los Angeles. Since 2012, this half-mile stretch of Avalon Boulevard had logged 396 crashes, injuring 170 and killing three.
Olivares, 27, a civil engineer for the city of Los Angeles, became the fourth fatality when he was hurled across the street, hit by a second car, and instantly killed. Rivas Cruz was transported to a hospital, where she remained in a coma for two weeks. Once awake, the elementary school teacher underwent a series of reconstructive surgeries to repair her arm, jaw, and legs.
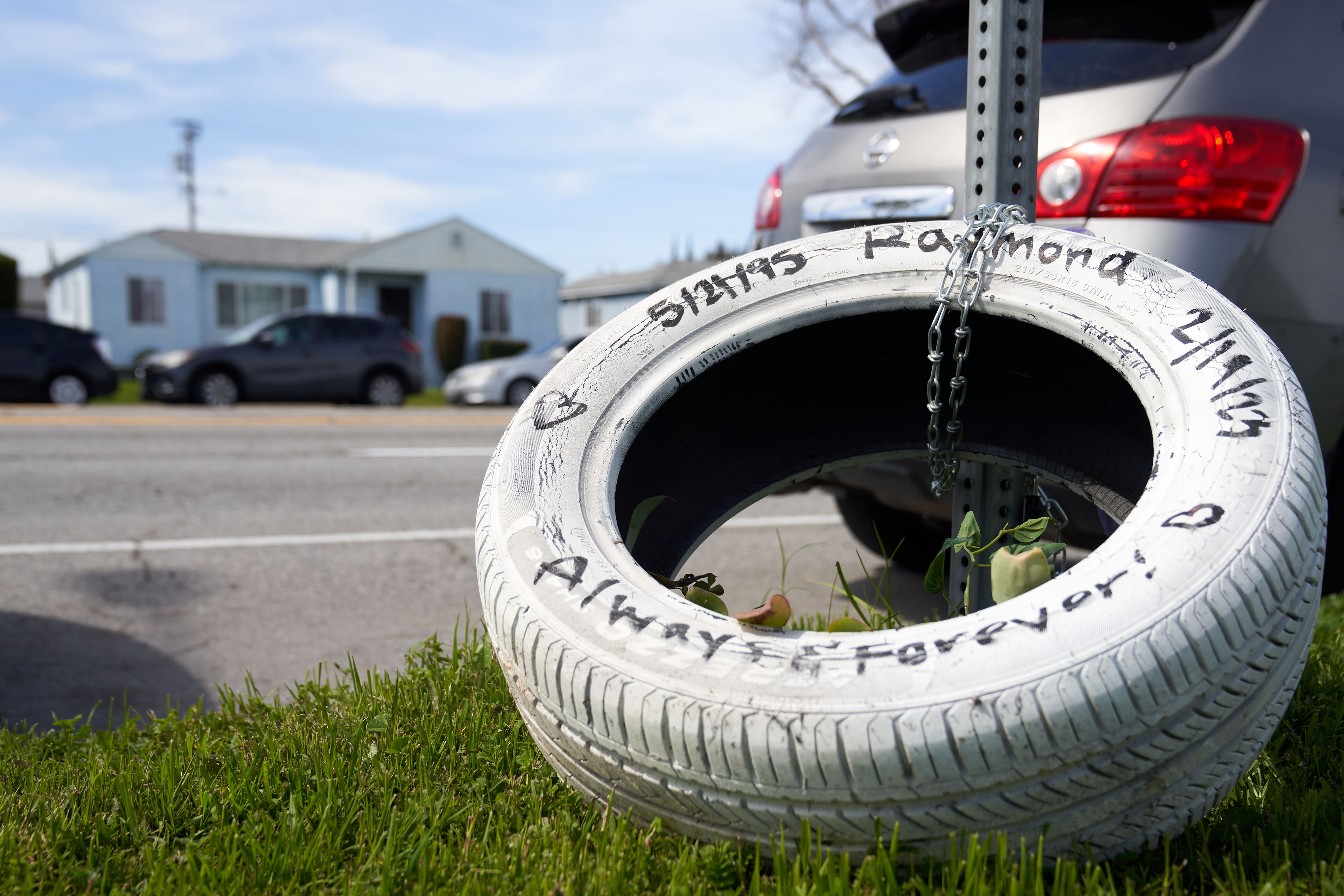


In the aftermath of the February 2023 crash, the county installed protective steel posts midway across the street. But residents, who had sought a platformed center divider and speed cameras, said that wasn’t enough.
“It’s just a band-aid on a cut. This is supposed to solve it, but it doesn’t, and that is what hurts,” said Rivas Cruz, who now at age 28 walks with a cane and lives with chronic pain. “I go to sleep, and I’m like, ‘It’s just a dream, it’s just a dream.’ And it’s not.”
The nation’s road system covers 4 million miles and is governed by a patchwork of federal, state, and local jurisdictions that often operate in silos, making systemic change difficult and expensive. But amid the highest number of pedestrians killed in decades, localities are pushing to control how speed limits are set and for more accountability on road design. This spring, New York and Michigan passed laws allowing local jurisdictions to lower speed limits. In Los Angeles, voters approved a measure that forces the city to act on its own safety improvement plan, mandating that the car-loving metropolis redesign streets, add bike lanes, and protect cyclists, transit riders, and pedestrians.
Still, there’s plenty of political resistance to speed enforcement. In California’s Statehouse, Sen. Scott Wiener (D-San Francisco) proposed requiring GPS-equipped smart devices in new cars and trucks to prevent excessive speeding. But after pushback, the state lawmaker watered down his bill to require all vehicles sold in the state starting in 2032 to have only warning systems that alert drivers when they exceed the speed limit by more than 10 mph.
Although the Biden administration is championing Vision Zero — its commitment to zero traffic deaths — and injecting more than $20 billion in funding for transportation safety programs through the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, road safety advocates and some lawmakers argue that the country is still far from making streets and vehicles safe, or slowing drivers down.
“We are not showing the political will to use the proven safety tools that exist,” said Leah Shahum, founder of Vision Zero Network, a nonprofit organization advancing Vision Zero in communities across the country.
Still a Crisis
The need for safer roads took on urgency during the covid pandemic. Fatalities rose even as lockdown mandates emptied streets. In 2022, more than 42,500 people died on American roads, and at least 7,522 pedestrians were fatally struck — the highest tally of pedestrian deaths in more than four decades.
Experts cite several reasons for the decline in road safety. During the lockdowns, reckless driving increased while traffic enforcement declined. SUVs and trucks have become larger and heavier, thus deadlier when they hit a pedestrian. Other factors persist as streets remain wide to accommodate vehicles, and in some states speed limits have gradually increased.
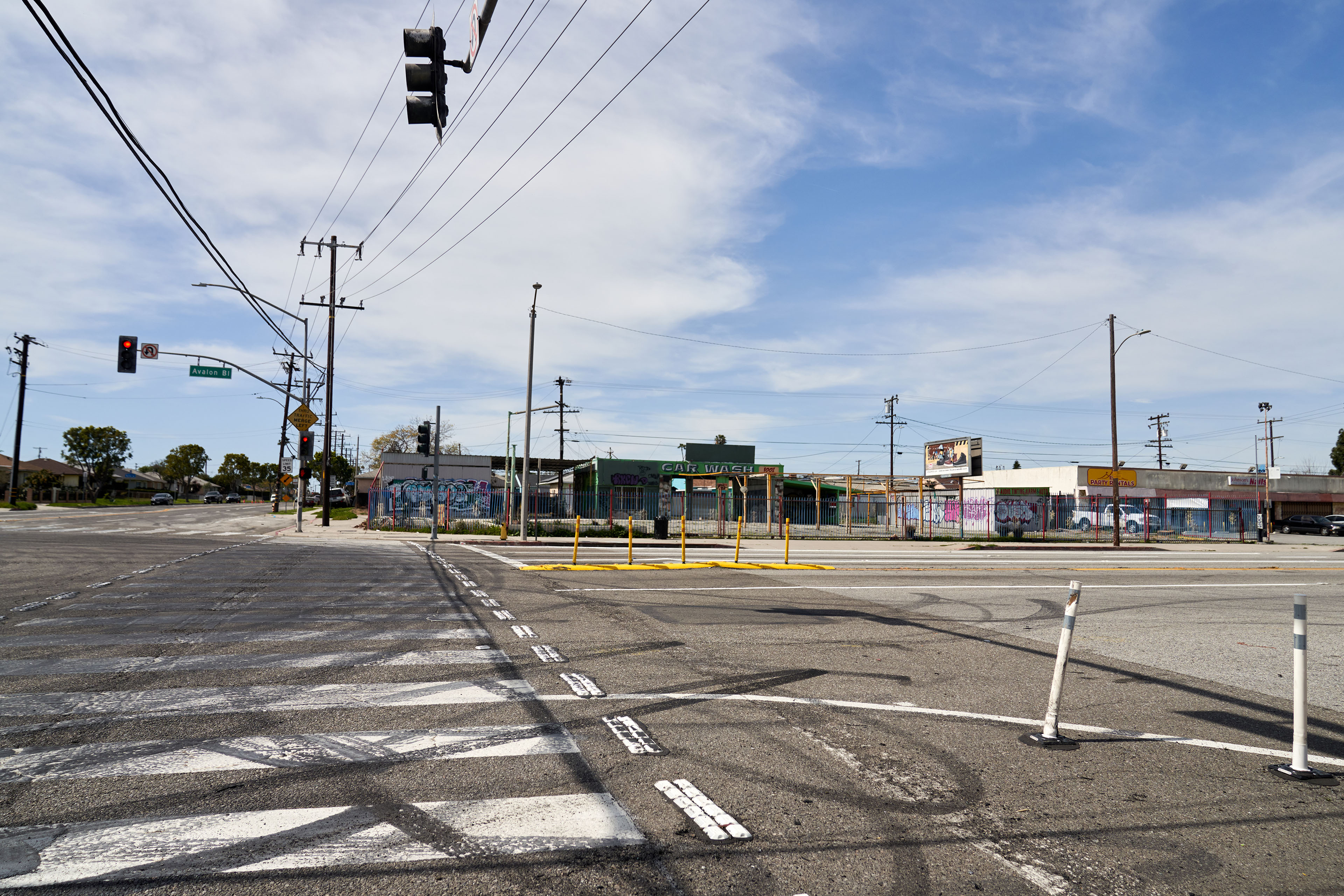


Early estimates of motor vehicle fatalities show a slight decrease from 2022 to 2023, but pedestrian fatalities are still notably above pre-pandemic numbers. “It’s an encouraging start, but the numbers still constitute a crisis,” Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg wrote in February of roadway deaths.


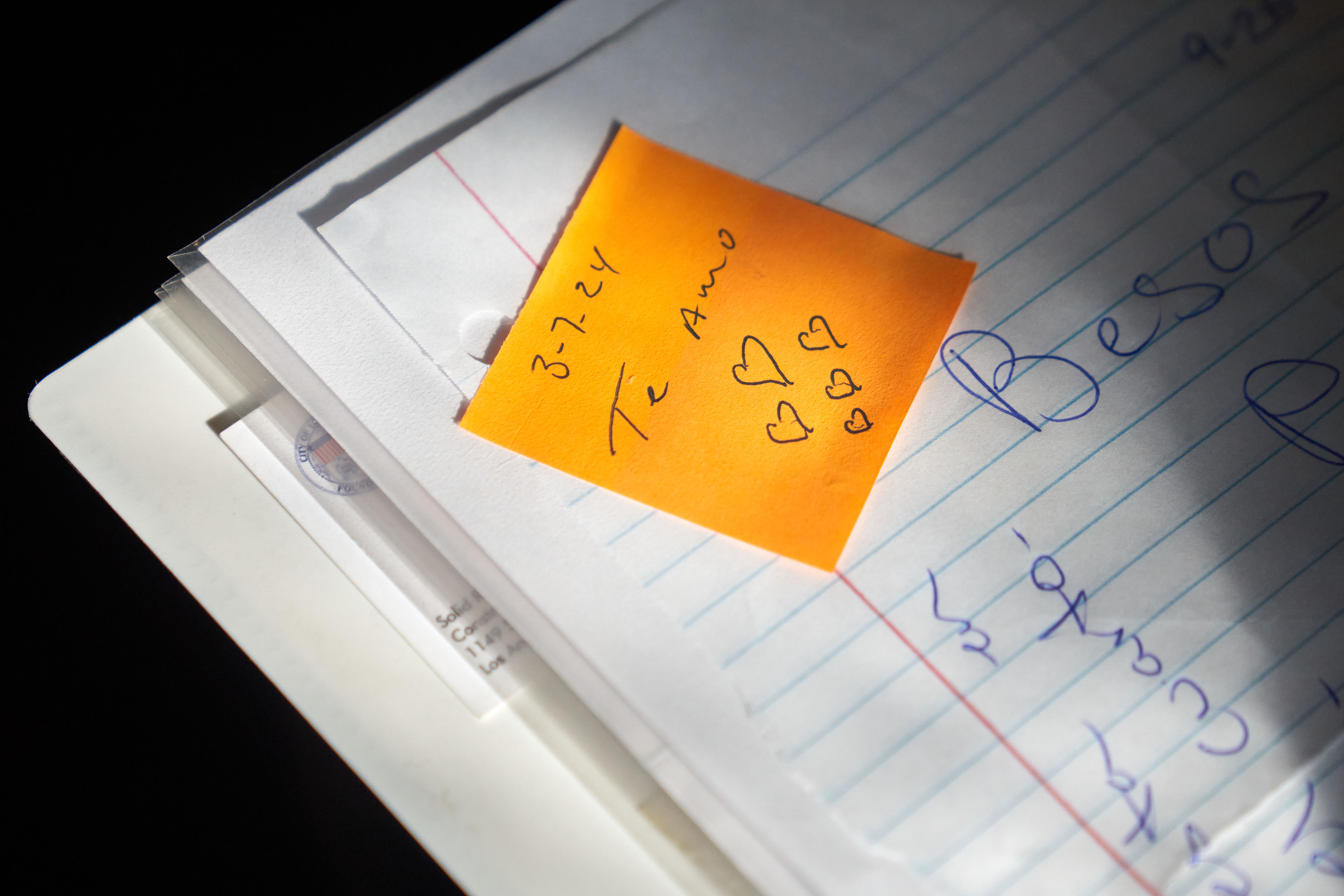


 .
.
 just saw this the other day. absolutely disgraceful
just saw this the other day. absolutely disgraceful