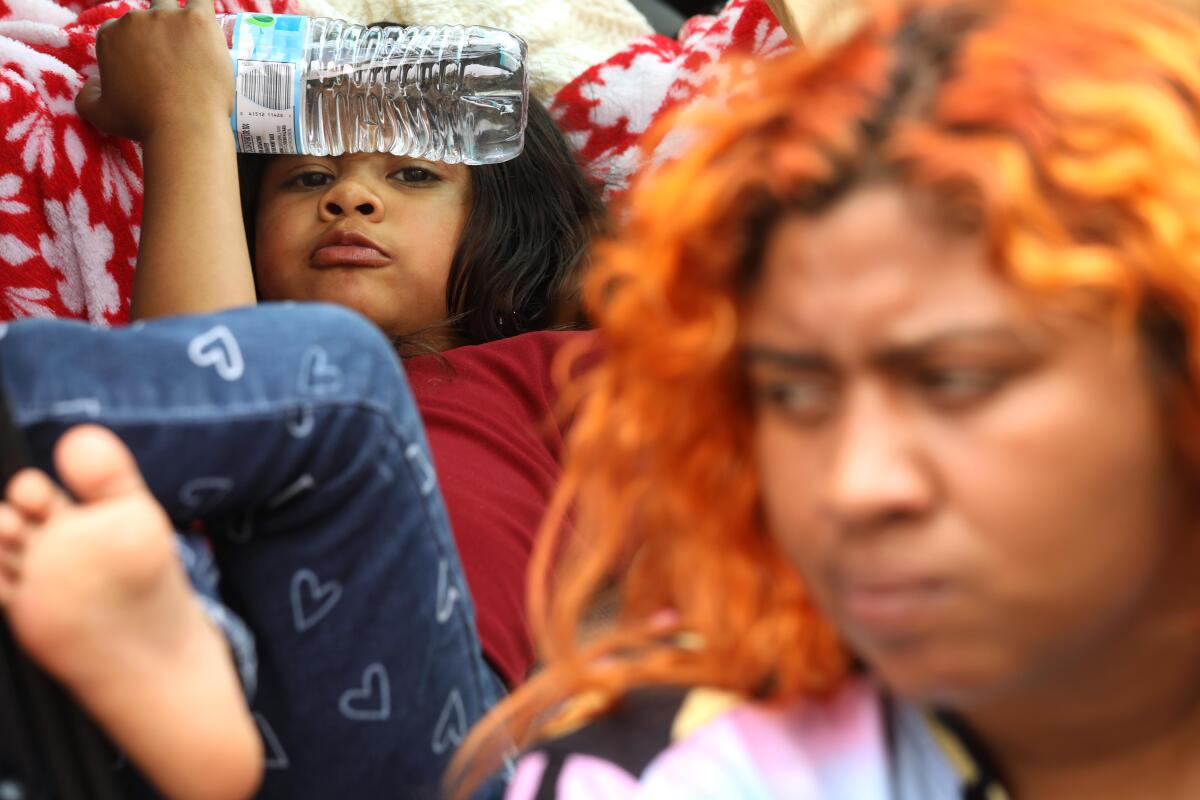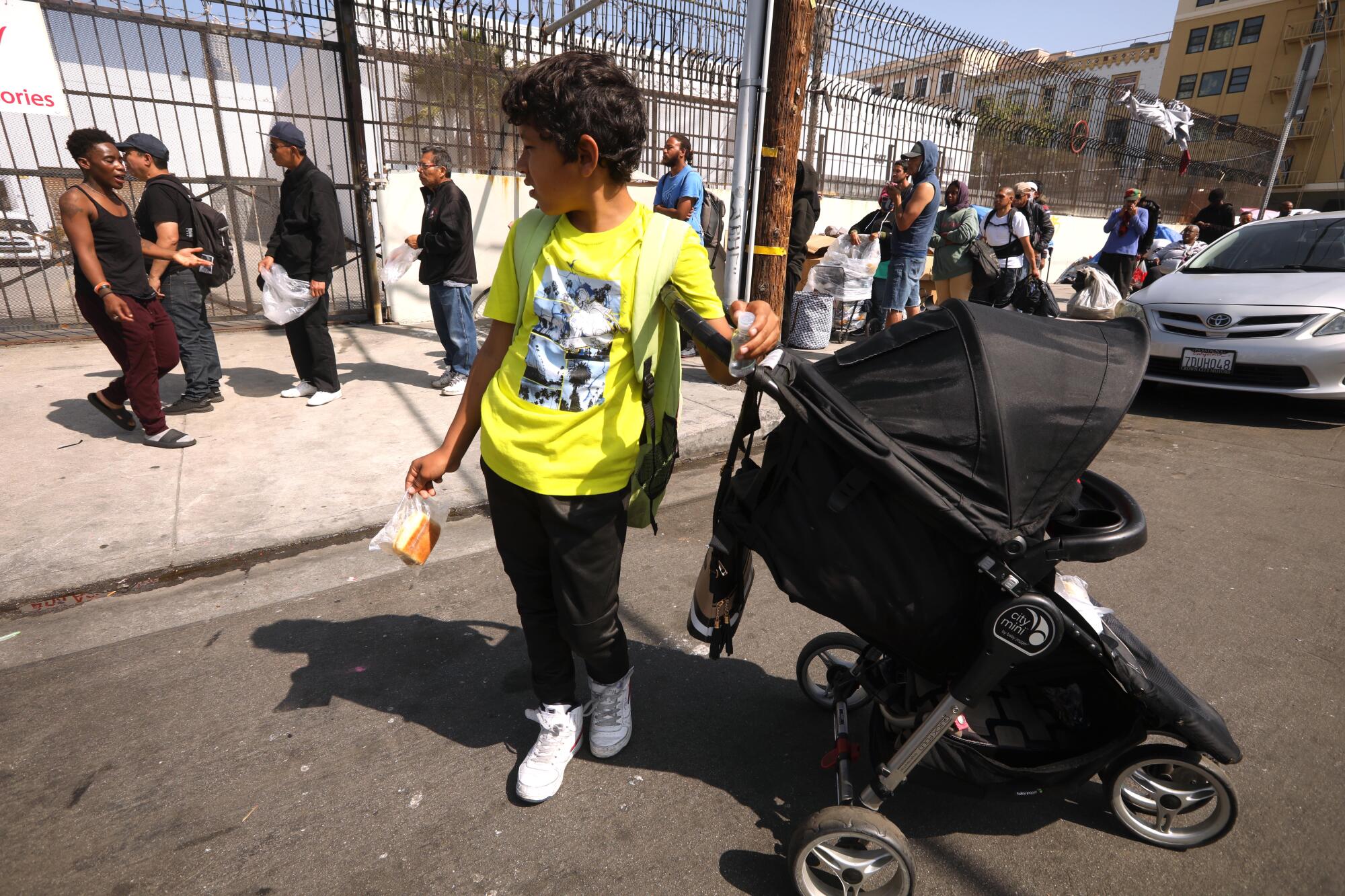Hundreds of children live on Skid Row. Can L.A. do more for them?
Advocates believe the number of children living on Skid Row will remain high as families in need of shelter confront a city with insufficient options.
Hundreds of children live on Skid Row. Can L.A. do more for them?

By Paloma EsquivelStaff Writer
Photography by
Genaro Molina
June 10, 2024 3 AM PT
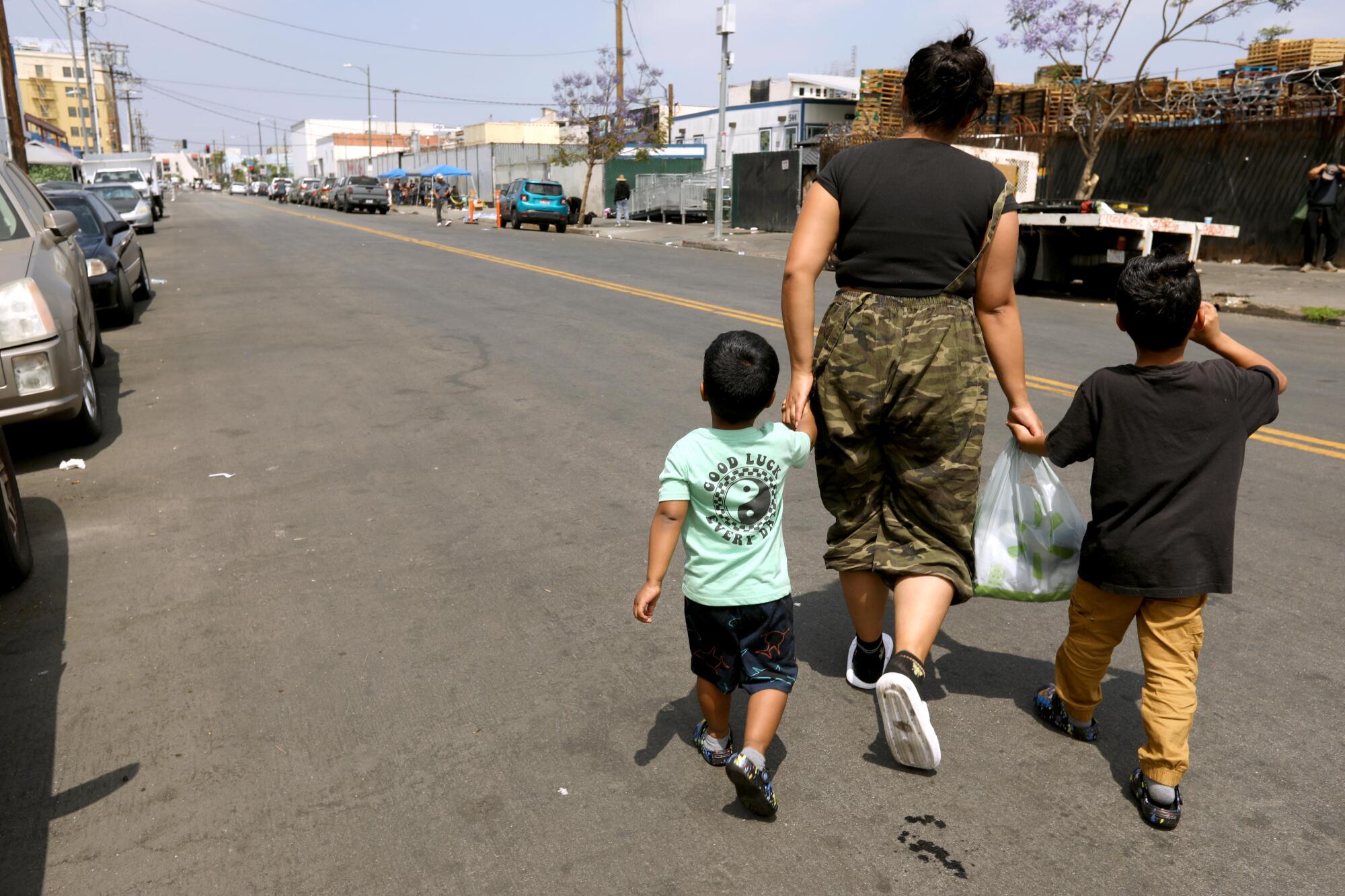
In the mornings, just past 7:30, dozens of children on Skid Row start making their way to school in the June gray.
For younger ones, the trip is somewhat easier.
A yellow bus pulls up not far from Union Rescue Mission and picks up kids who attend Ninth Street Elementary, a Los Angeles Unified School District school.
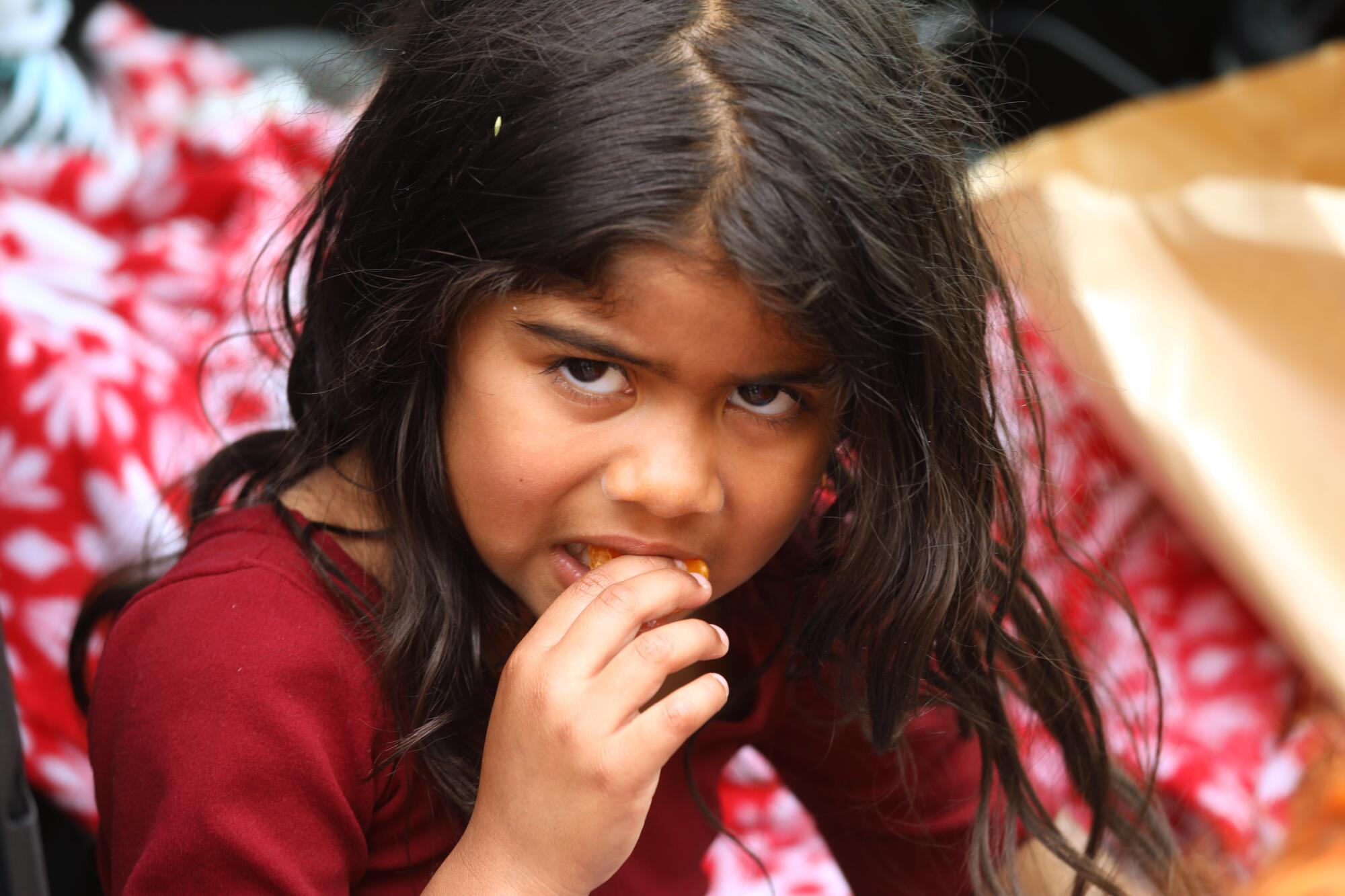

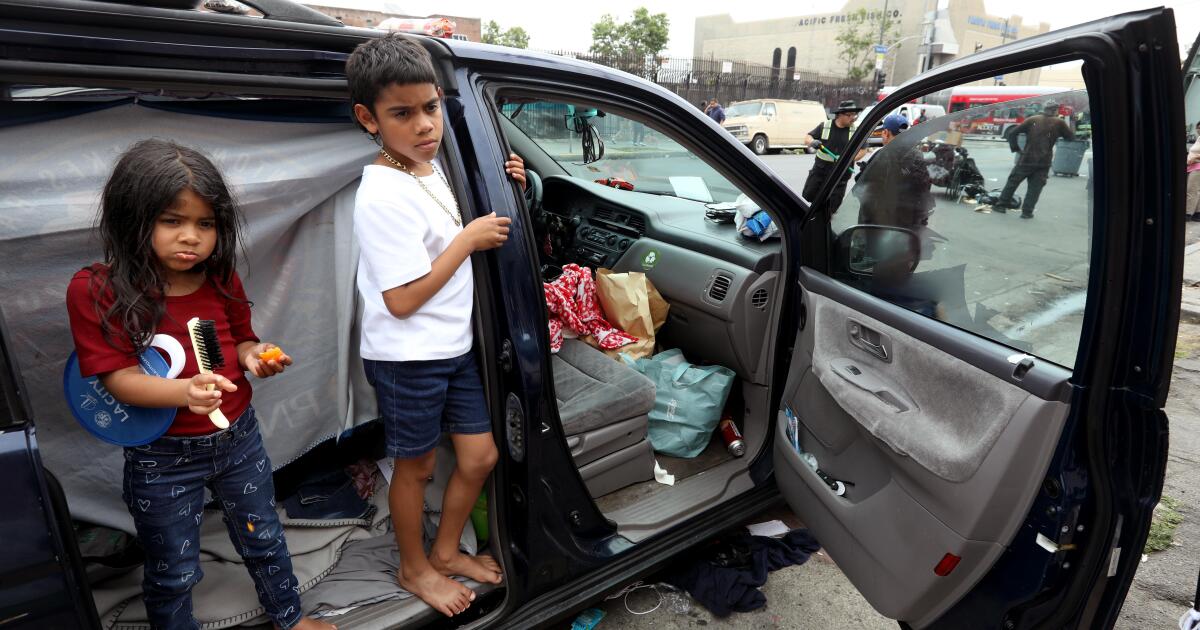
Celeste, 5, eats a tangerine inside the family car on Skid Row in Los Angeles.
The middle schoolers study on the same campus. But theirs is a charter school and they don’t have a bus. To get to school they walk several blocks, past tents and tarp shelters, careful not to step on discarded needles or human waste.
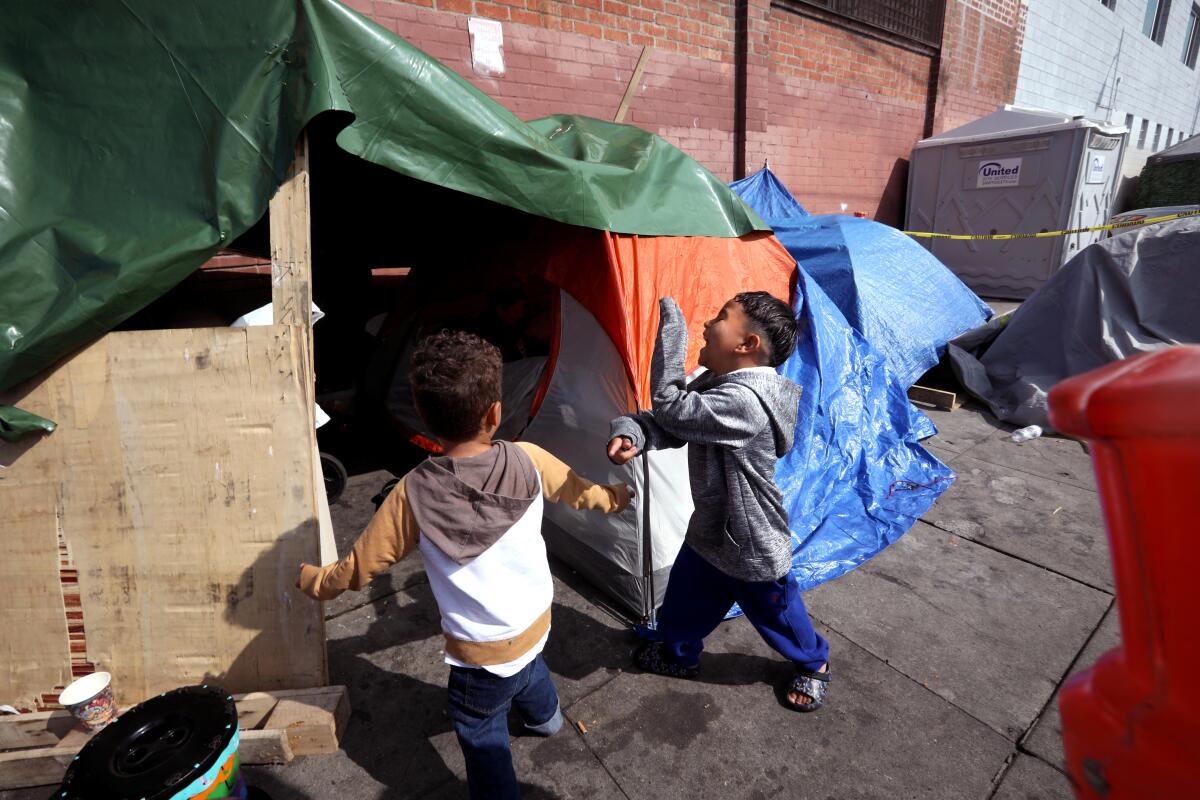
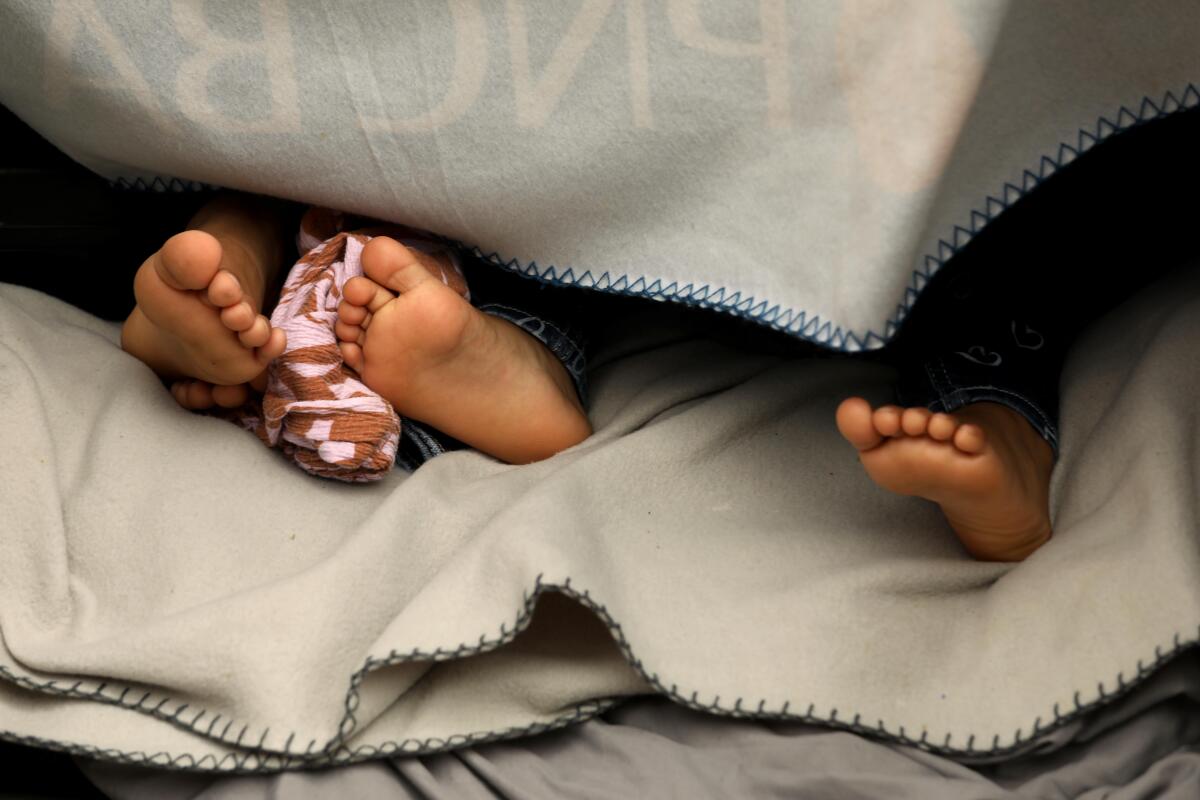
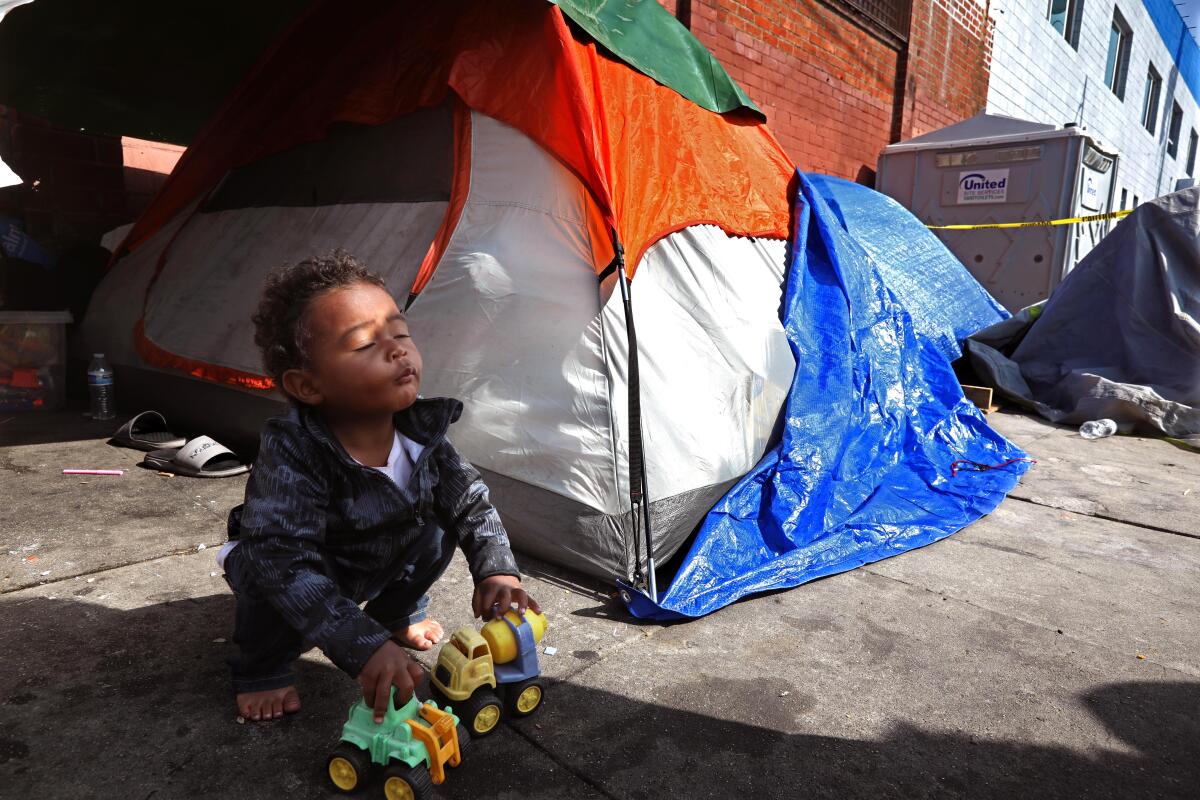
Skid Row, if it must be said, is not a place for children. And yet there are more than 100 families living there now, with more than 200 children. The large majority stay at the mission — a privately funded shelter that is the only one in the neighborhood that accepts families.
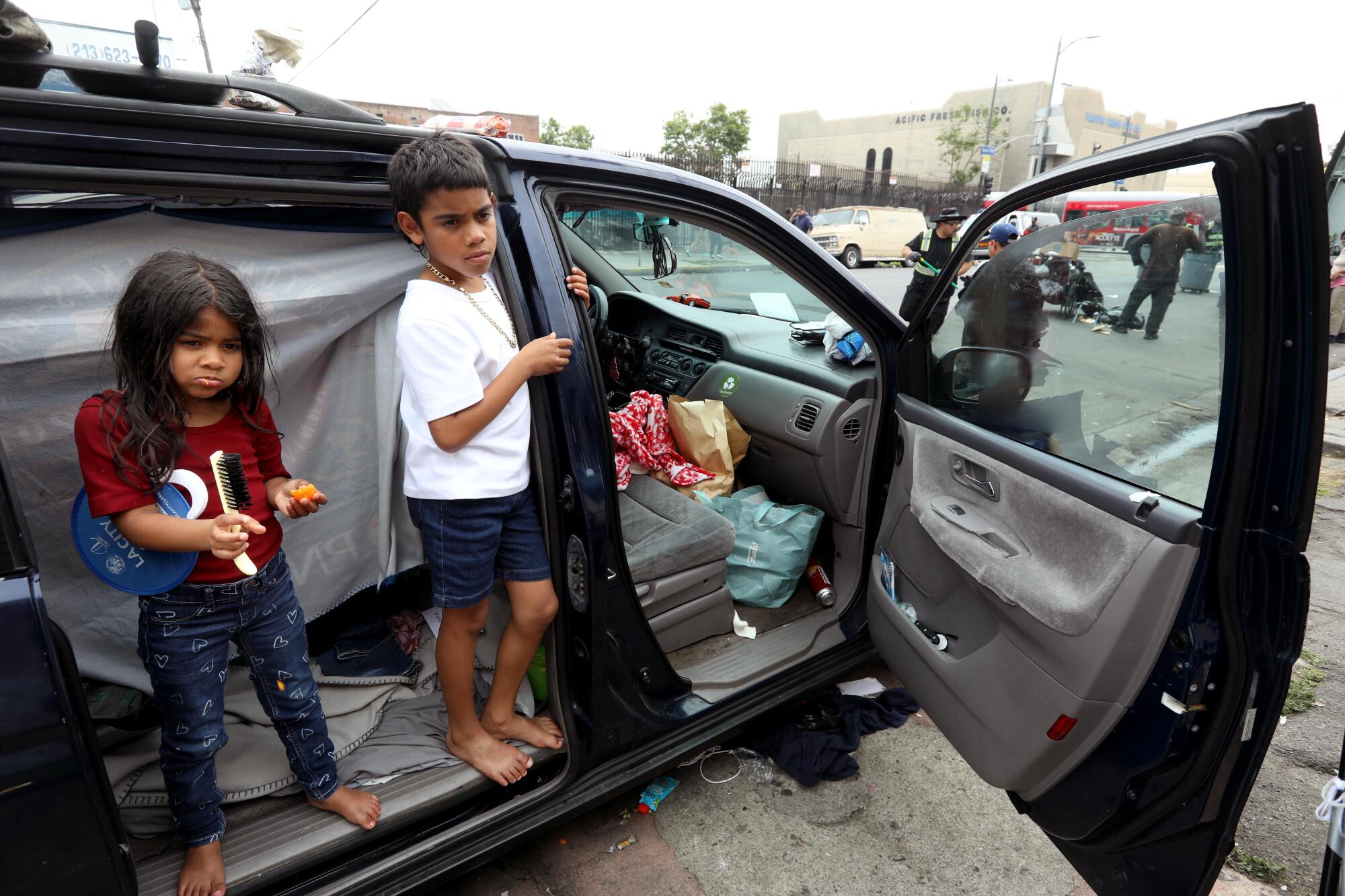
A smaller number live in tents, often on Towne Avenue, which has become the place of last resort for families that have run out of options.
Advocates say they believe the number of children in the neighborhood isn’t going down any time soon, as families in desperate need of shelter confront a city with insufficient options. And some are asking whether there are immediate steps that city and other officials should take to improve the quality of life for children on Skid Row as long as they remain.
In a city with a school district that has 1,300 buses, could someone ensure that all children have access to bus transportation for school? Is it possible to provide parents with day care for young children so they can work? Can there be play groups for kids living in the shelter? What about transportation to parks, after-school programs or summer classes?
“How do we create a model here on Skid Row that brings those things that every healthy neighborhood has? How do we do it in a way that’s family friendly, and easy to access?” asked Sam Joo, vice president of student and community services for the nonprofit organization Para Los Niños.

Dylan, 8, stands at the entrance to a tent he shares with his mother, Jaidelin Chacon. Sometimes the family spends the night in their car, parked along the sidewalk.
Many, though not all, of the families in the neighborhood are newly arrived migrants who crossed the border and made their way to L.A., sometimes on buses paid for, they say, by various groups in San Diego, Texas and Arizona.
The Los Angeles Homeless Services Authority (LAHSA) recently established two new interim housing facilities at former winter shelter sites in South Los Angeles to help house families living on Skid Row. Those sites, which have a total of 18 units, are already at capacity, officials said. Other families have been housed in motels.
Beyond the city of L.A., the county has also seen an overall increase in the number of families in the homeless system in recent months. There were more than 900 additional new families in the first half of this fiscal year compared with the previous one, for a total of nearly 3,500, according to county data.
Estela Lopez, executive director of the Downtown Industrial District BID, said local businesses have been raising alarms about the number of children on Skid Row for several months. The area is an industrial one, where trucks begin arriving before dawn to the many wholesale and import/export businesses that line the streets.
Forty percent of the streetlights in the neighborhood don’t work, creating a dangerous situation for children who are bound to run and play where they live, Lopez said.

A man sits on a sidewalk as dusk settles over Skid Row in downtown Los Angeles in March 2023.
Then there are dangers that are inherent to the neighborhood.
“Skid Row is violent,” Lopez said. “There’s rampant untreated mental illness on the street. High levels of drug addiction. It’s dangerous for anyone.”
Many of the resources that exist in the neighborhood were designed to serve adults who might have substance abuse problems or mental health struggles, not newly arrived migrant families with children, she said.
“This is an entirely new population that needs an entirely new solution,” she said.
Para Los Niños, which was started after its founder read a 1979 Los Angeles Times article describing the lives of migrant children on Skid Row, has been asking local officials for funding to coordinate and increase services for children and families on Skid Row and will soon be preparing a proposal to design a model to help address some of the immediate needs confronting families.
“Whether it’s an after-school program, a parenting program, even things like potty training. If that is a barrier for a child to enter a preschool, then let’s just address that barrier,” Joo said. “Provide us the resources so we can design this model that we feel is going to be more beneficial to families.”
Parents of young children on Skid Row say they sometimes struggle to work because they don’t have a place to leave their babies and toddlers. Many early education centers do not accept children until they are potty trained — but potty training when living in a tent or a shelter with hundreds of other people can be nearly impossible.
Para Los Niños’ own Skid Row early education program, located on 6th Street, cares for children starting in infancy, offering an array of services including family support, mental health assistance and help preparing children for school. But it has a waitlist more than 100 children long.
At Charter Middle School, which is also run by Para Los Niños and serves children who live on Skid Row, about 20% of students are homeless, said Principal Chris Coyle. And more arrive every week.